Autonomous Vehicle Data Encryption
With Autonomous Vehicle Data Encryption at the forefront, embark on a journey to explore the vital role of securing data in autonomous vehicles. From potential risks to innovative encryption techniques, uncover the keys to a safer and smarter future in mobility.
Overview of Autonomous Vehicle Data Encryption
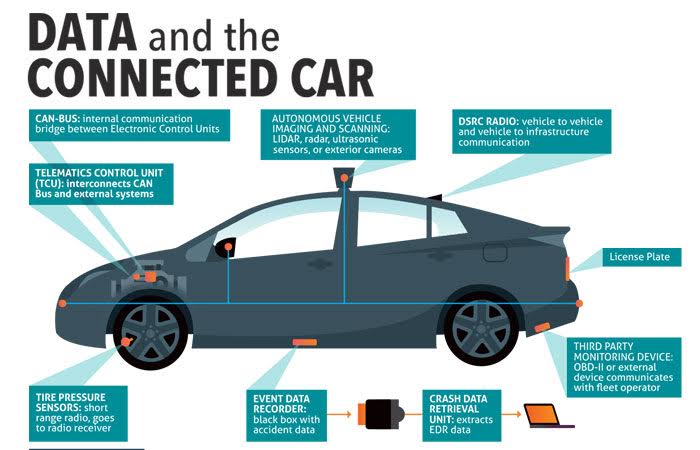
Data encryption plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and privacy of autonomous vehicles. By encrypting sensitive data, such as location information, driving patterns, and vehicle diagnostics, manufacturers and users can mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and potential cyber-attacks.
Importance of Data Encryption in Autonomous Vehicles
Data encryption in autonomous vehicles is essential to protect sensitive information from hackers and cyber threats. Without proper encryption, unauthorized individuals could potentially access and manipulate critical data, compromising the safety and functionality of the vehicle.
Examples of Sensitive Data that Require Encryption
- Location data: GPS coordinates and routes taken by the vehicle.
- Driving patterns: Speed, acceleration, braking behavior, and lane changes.
- Vehicle diagnostics: Maintenance information, performance metrics, and system updates.
Potential Risks of Inadequate Data Encryption
Inadequate data encryption in autonomous vehicles can lead to severe consequences, including:
-
Data theft: Hackers could steal sensitive information, compromising user privacy and safety.
-
Tampering with data: Unauthorized access could result in altered driving patterns or malicious commands to the vehicle’s systems.
-
Malware attacks: Vulnerable systems may be targeted by malware, leading to system failures or loss of control.
Encryption Techniques for Autonomous Vehicles
Encryption plays a crucial role in securing data transmitted and stored within autonomous vehicles. Various encryption methods are employed to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information. Let’s explore different encryption techniques used in autonomous vehicles, compare symmetric and asymmetric encryption, and discuss the role of blockchain technology in enhancing data security.
Symmetric Encryption, Autonomous Vehicle Data Encryption
Symmetric encryption, also known as secret key encryption, involves the use of a single key to both encrypt and decrypt data. In autonomous vehicles, symmetric encryption is commonly used for its efficiency and speed in processing large amounts of data. However, the challenge lies in securely sharing the encryption key between communicating parties to prevent unauthorized access.
Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption, or public key encryption, utilizes a pair of keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. This method enhances security in autonomous vehicles by allowing data to be securely transmitted over public networks without the need to share the private key. Asymmetric encryption is often used for key exchange and digital signatures in autonomous vehicle communication protocols.
Role of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and tamper-resistant platform for securing autonomous vehicle data. By storing encrypted data in a distributed ledger, blockchain ensures data integrity and transparency. Smart contracts can be implemented to automate secure data transactions and access control, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized modifications. The immutability of blockchain makes it an ideal solution for enhancing the security of autonomous vehicle data in a connected environment.
Regulations and Standards for Data Encryption in Autonomous Vehicles

Data encryption in autonomous vehicles is subject to various regulatory frameworks that aim to protect sensitive information and ensure data security. Compliance with data protection laws plays a crucial role in the development of autonomous vehicles, as it helps build trust among users and stakeholders. However, implementing encryption standards across different regions comes with its own set of challenges.
Regulatory Frameworks for Data Encryption
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): The GDPR sets strict guidelines for the collection, storage, and processing of personal data, including data gathered by autonomous vehicles. Companies must ensure that data encryption is used to protect this information.
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): Similar to GDPR, CCPA requires businesses to implement security measures such as encryption to safeguard consumer data collected by autonomous vehicles.
Impact of Compliance with Data Protection Laws
- Enhanced Data Security: By complying with data protection laws, companies can enhance the overall security of autonomous vehicle data, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Improved Consumer Trust: Compliance with regulations instills confidence in consumers regarding the privacy and security of their data, leading to increased acceptance and adoption of autonomous vehicles.
Challenges of Implementing Encryption Standards
- Interoperability Issues: Different regions may have varying encryption standards, making it challenging to ensure seamless interoperability between autonomous vehicles operating in different locations.
- Compliance Costs: Implementing encryption standards can be costly, especially for companies operating on a global scale and needing to adhere to multiple regulatory frameworks simultaneously.
Cybersecurity Threats and Solutions for Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles face a myriad of cybersecurity threats due to their reliance on complex systems and connectivity. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the software or communication channels to gain unauthorized access, potentially leading to disastrous consequences. To combat these threats, robust data encryption techniques are essential to safeguard sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access.
Common Cyber Threats Faced by Autonomous Vehicles
- Malware and ransomware attacks targeting vehicle systems.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks disrupting communication networks.
- Hacking of sensors or cameras to manipulate perception data.
- Unauthorized access to vehicle control systems.
Strategies to Mitigate Cybersecurity Risks through Data Encryption
- Implement end-to-end encryption to secure data transmission.
- Use strong encryption algorithms and keys to protect data at rest.
- Regularly update software and security patches to address vulnerabilities.
- Employ secure boot mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access to vehicle systems.
Role of AI in Enhancing Cybersecurity Measures for Autonomous Vehicles
AI plays a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity for autonomous vehicles by enabling proactive threat detection and response. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify anomalous behavior and potential security breaches in real-time. Additionally, AI-powered systems can continuously adapt and improve cybersecurity measures based on evolving threats, ensuring robust protection against cyber attacks.
Helpful Answers
What types of data in autonomous vehicles require encryption?
Sensitive data such as GPS locations, driver information, and vehicle diagnostics require encryption to prevent unauthorized access.
How does compliance with data protection laws impact autonomous vehicle development?
Compliance with data protection laws ensures that autonomous vehicle manufacturers prioritize data security, leading to safer and more reliable vehicles.
What are some common cybersecurity threats faced by autonomous vehicles?
Common threats include hacking attempts, ransomware attacks, and data breaches that can compromise the safety and functionality of autonomous vehicles.
How does AI enhance cybersecurity measures for autonomous vehicles?
AI can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time to detect anomalies and potential threats, strengthening cybersecurity defenses in autonomous vehicles.